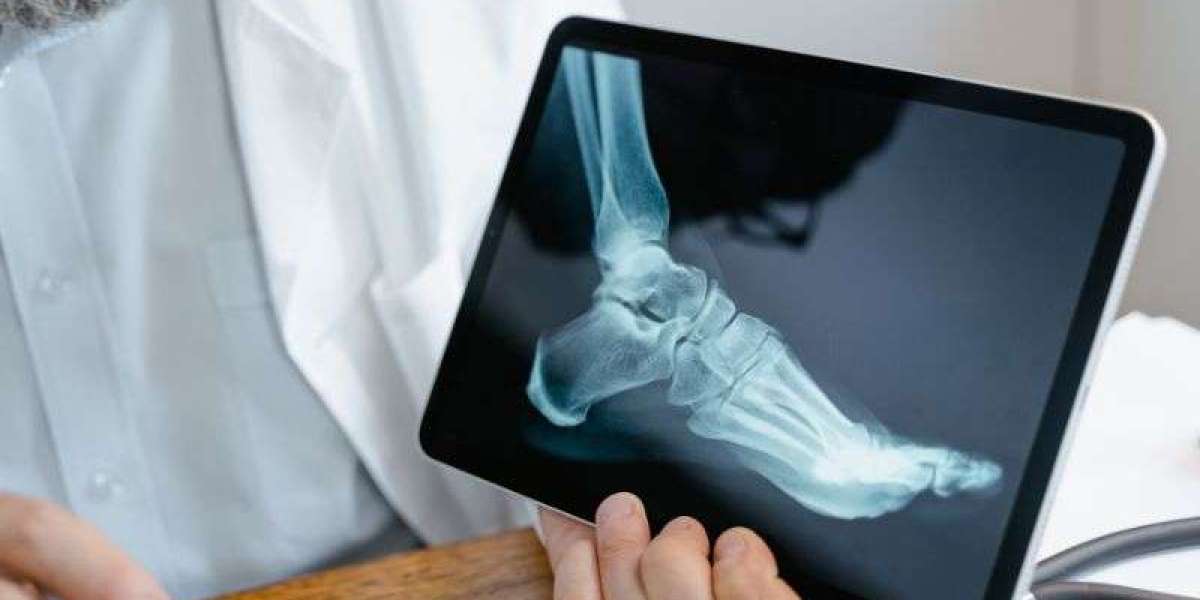
Ankle fractures are among the most common types of bone injuries, often resulting from sports activities, falls, or accidents. Ankle fractures can range from simple hairline cracks to complex breaks involving multiple bones. Regardless of the severity, it’s crucial to address the injury promptly and follow an effective treatment plan to ensure proper healing. This comprehensive overview will guide you through ankle fracture recovery time, treatment options, and the steps to manage leg ankle fracture treatment successfully.
Understanding Ankle Fractures
An ankle fracture occurs when one or more of the bones in the ankle joint break. The ankle is a complex structure consisting of three bones: the tibia (shinbone), the fibula (the smaller bone next to the tibia), and the talus (a small bone that sits between the leg bones and the heel). Ankle fractures can be classified into different types depending on the location and severity of the break. The most common causes include:
- Sports injuries: Particularly in activities like basketball, soccer, and skiing.
- Falls: Especially from a height or slipping on a slick surface.
- Car accidents: Resulting in high-energy impacts.
Symptoms of an Ankle Fracture
The symptoms of an ankle fracture vary depending on the severity but commonly include:
- Pain: This is usually severe and can be felt immediately after the injury.
- Swelling: The ankle will likely swell, often quickly after the injury occurs.
- Bruising: Bruising may appear around the ankle, especially in more severe fractures.
- Deformity: In some cases, the ankle may look visibly deformed, and bones may even protrude through the skin.
- Inability to bear weight: Walking or standing will likely be very difficult or impossible due to pain and instability.
Diagnosing an Ankle Fracture
To properly diagnose an ankle fracture, healthcare providers rely on a physical examination, patient history, and imaging tests. An X-ray is the most common method for visualizing bone fractures, while CT scans may be used for more complex cases. The goal of diagnosing an ankle fracture is to determine the exact nature of the injury and formulate a treatment plan accordingly.
Leg Ankle Fracture Treatment
Once diagnosed, the treatment of an ankle fracture depends on the severity and type of fracture. Leg ankle fracture treatment can be broadly categorized into non-surgical and surgical approaches.
Non-Surgical Treatment
For simple, non-displaced fractures where the bones are not out of place, non-surgical treatment may be sufficient. The general approach involves:
- Rest and Elevation: The ankle should be rested, and the leg should be elevated to reduce swelling.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help control swelling and numb pain.
- Immobilization: The ankle is typically immobilized in a cast or brace to prevent further movement of the bones.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen are often used to manage pain during the initial stages of recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Once the fracture begins to heal, physical therapy may be recommended to restore strength, mobility, and flexibility to the joint.
Surgical Treatment
In more severe cases, where the fracture is displaced (the bones are out of alignment) or involves multiple fractures, surgery may be necessary to properly realign the bones and ensure proper healing. Surgical options include:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): This procedure involves realigning the fractured bones and securing them with screws, plates, or rods to hold the bones in place during the healing process.
- External Fixation: In rare cases, external fixators may be used, particularly for fractures with severe soft tissue damage. This involves placing a frame outside the leg to stabilize the bones.
Following surgery, the recovery process may be longer, and additional rehabilitation may be required to regain full ankle function.
Ankle Fracture Recovery Time
The ankle fracture recovery time varies based on the type of fracture and the treatment method. For most patients, recovery typically takes between 6 and 12 weeks for bone healing, but full recovery, including regaining strength and range of motion, can take several months.
Factors that influence recovery time include:
- The severity of the fracture: Simple fractures tend to heal faster, while complex or displaced fractures may take longer.
- Treatment method: Non-surgical fractures tend to heal more quickly, while surgical interventions can require more time for the bones to heal properly.
- Age and health: Younger, healthier individuals may experience quicker healing than older adults or those with underlying medical conditions.
- Adherence to rehabilitation: Patients who follow their physical therapy regimen and exercise plan typically experience faster recovery times and better functional outcomes.
It's important to note that during the recovery process, weight-bearing on the affected ankle is often restricted for a few weeks. Once the bones have sufficiently healed, a gradual increase in activity and weight-bearing will be recommended.
Potential Complications
While the majority of ankle fractures heal successfully with proper treatment, complications can sometimes arise, especially if the injury is severe or if treatment is delayed. Some potential complications include:
- Nonunion or malunion: This occurs when the bones do not heal correctly or at all, leading to long-term instability.
- Infection: This is a risk in cases requiring surgery.
- Post-traumatic arthritis: Long-term joint stiffness and pain can occur, especially if the fracture affects the articular surface of the bones.
- Nerve or blood vessel damage: Fractures that are more severe may result in nerve or blood vessel injury, leading to further complications.
Preventing Ankle Fractures
While some ankle fractures are unavoidable, you can take steps to reduce your risk:
- Strengthen the muscles around your ankle through exercise to provide better support.
- Wear supportive footwear that fits properly.
- Be cautious when walking on slippery surfaces or uneven ground.
- Warm up properly before engaging in sports or physical activity to prevent injury.
Conclusion
Ankle fractures, while common, can be treated successfully with the right care and attention. Whether you're dealing with a simple fracture or a more complex injury, timely and effective leg ankle fracture treatment is crucial for a successful recovery. Patience during the ankle fracture recovery time is key, as it can take several weeks or months for the bones and joints to fully heal. With proper medical care, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, most individuals make a full recovery and can return to normal activities.
for more(click here)