Pentene is a vital organic compound widely used in the petrochemical industry as a key component for producing various chemicals, including plastics, synthetic rubber, and additives. With the growing demand for these materials across multiple sectors, the production of pentene has become a critical part of global manufacturing. Establishing a pentene manufacturing plant offers promising business opportunities, especially with the increasing need for raw materials in industries like automotive, packaging, and construction. This project report delves into the essential aspects of setting up and operating a pentene manufacturing facility, including raw material sourcing, production processes, required equipment, and market trends.
Understanding Pentene and Its Applications
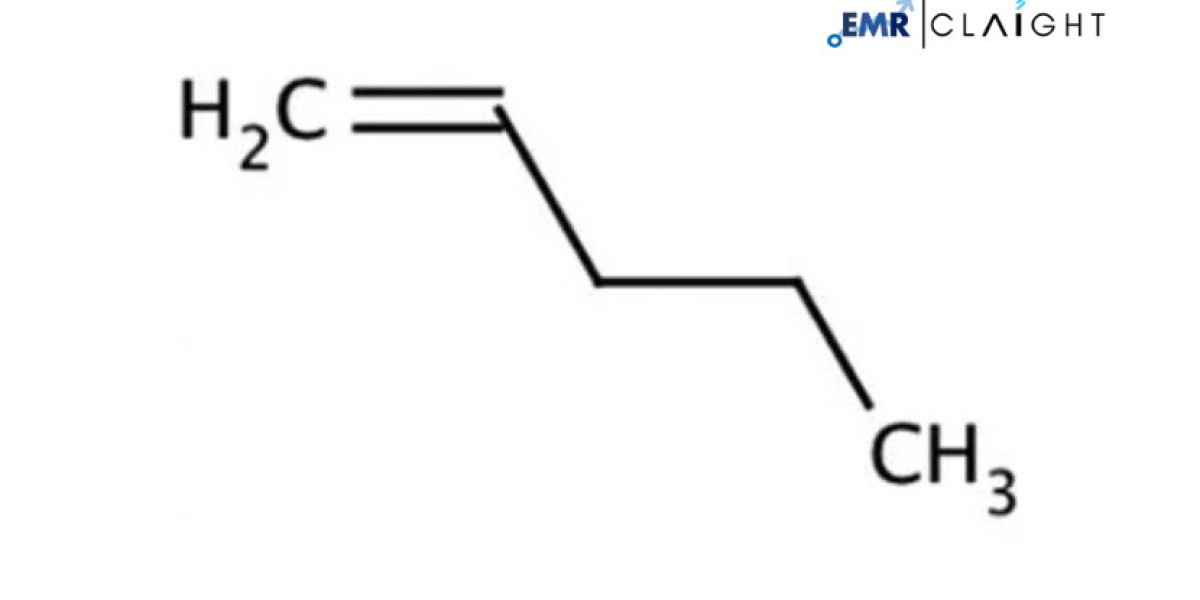
Pentene is an alkene with a five-carbon structure and is primarily used as a building block for various chemical reactions. It exists in different isomeric forms, including 1-pentene, 2-pentene, and iso-pentene, each of which has distinct applications. These different forms of pentene are utilized in diverse industries for their ability to act as a precursor to more complex chemical compounds.
a. Production of Polyethylene and Other Plastics
One of the most important applications of pentene is in the production of polyethylene, which is one of the most widely used plastics in the world. Polyethylene is used in packaging, containers, plastic bags, and numerous other consumer goods. Pentene is used to create low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and other copolymers, making it crucial in the plastic manufacturing industry.
b. Synthetic Rubber Production
Pentene is also an essential component in the production of synthetic rubber, specifically in the manufacturing of butyl rubber. Butyl rubber, which is used in tire manufacturing and the production of industrial products such as gaskets, seals, and adhesives, relies on pentene as a key monomer.
c. Chemical Intermediates and Additives
Pentene serves as an intermediate in the production of various chemical compounds, including plasticizers, detergents, and lubricants. Its versatility makes it a valuable compound in the production of high-performance additives used in industries such as automotive, construction, and personal care.
d. Pharmaceuticals and Agrochemicals
Pentene is also used in the synthesis of certain pharmaceutical compounds and agrochemicals. While these applications account for a smaller portion of the market, they contribute to the compound’s widespread industrial importance.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@ https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/pentene-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Setting Up a Pentene Manufacturing Plant
Establishing a pentene manufacturing plant requires careful planning and investment in several key areas. From raw material sourcing to production methods and regulatory compliance, the setup process is multifaceted. Here are the major aspects to consider:
a. Location and Infrastructure
Selecting the right location for a pentene manufacturing facility is crucial for minimizing operational costs and ensuring logistical efficiency. Some important factors to consider include:
Proximity to Raw Materials: Pentene is derived from petroleum and natural gas, and having access to refineries or oil extraction facilities can reduce raw material transportation costs. Locations close to chemical production hubs or petroleum refineries can provide a stable supply of feedstocks.
Access to Transportation Routes: A well-connected location is essential for the efficient movement of raw materials and finished products. Ports, railways, highways, and airports should be accessible to ensure timely deliveries and distribution to markets.
Utility Availability: Pentene manufacturing requires significant amounts of energy, particularly heat and electricity, for various chemical processes. Ensuring that the location can provide a reliable supply of energy at competitive rates is vital for maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Regulations: Depending on the region, environmental regulations surrounding emissions, waste disposal, and chemical processing can vary. The chosen location should adhere to local environmental standards to avoid operational disruptions.
b. Raw Materials and Sourcing
The primary raw materials used in the production of pentene are derived from petroleum. These materials are obtained through processes such as cracking, which breaks down large hydrocarbons into smaller, more useful molecules.
Key raw materials involved in pentene production include:
Crude Oil or Natural Gas: The extraction of pentene typically starts with the cracking of petroleum fractions. The composition and quality of crude oil will affect the final output of pentene, so sourcing high-quality petroleum feedstock is critical.
Catalysts and Chemicals: Various catalysts are used in the cracking process to enhance reaction efficiency and yield. These include materials like silica-alumina, which promote the formation of pentene and other desired alkenes.
The efficient and cost-effective sourcing of these raw materials plays a vital role in keeping production costs competitive.
c. Production Process for Pentene
The production of pentene typically involves several key chemical processes that break down larger hydrocarbons into smaller molecules. The most common method for pentene production is catalytic cracking, which is used in petroleum refineries to break down large hydrocarbons into a mixture of smaller alkenes, including pentene.
The general steps involved in the production of pentene include:
Crude Oil Distillation: In the first step, crude oil is heated in a distillation column to separate different hydrocarbon fractions. These fractions include lighter gases, naphtha, and heavier oils, which will be further processed.
Catalytic Cracking: Naphtha or other light fractions are fed into a cracking unit, where they are subjected to high temperatures and pressure in the presence of a catalyst. This process breaks down the large molecules into smaller alkenes, including pentene. The catalyst promotes the selective formation of pentene, making it one of the desired products in the cracking process.
Separation and Purification: After cracking, the mixture of products is passed through a series of separators and distillation columns to isolate pentene from other by-products. The pentene is then purified to remove any residual impurities.
Recovery and Refining: The final step in the production process involves further refining to ensure that the pentene meets the required purity specifications. This may include additional distillation or filtration processes.
d. Equipment and Technology Requirements
A pentene manufacturing plant requires various types of equipment to handle the complex chemical processes involved in its production. These include:
Cracking Units: These are the heart of the pentene production process. The cracking unit uses heat and pressure to break down larger hydrocarbons into smaller molecules like pentene.
Distillation Columns: Distillation is used to separate different hydrocarbon fractions based on their boiling points. Specialized distillation columns are required to isolate pentene from other by-products.
Catalyst Reactors: These reactors contain the catalysts that help drive the cracking process and improve the yield of pentene.
Filtration and Purification Systems: After separation, pentene is often purified to meet product specifications. This requires advanced filtration and purification technologies to remove impurities.
Storage Tanks: Pentene, as a volatile chemical, must be stored in specialized tanks designed to handle flammable and potentially hazardous substances.
e. Labor and Workforce Requirements
Operating a pentene manufacturing plant requires skilled personnel at various levels. The key workforce roles include:
Chemical Engineers: These professionals design and optimize the production process, ensuring the efficient and safe production of pentene.
Plant Operators: Operators are responsible for running the plant’s day-to-day operations, monitoring machinery, and maintaining control over the chemical processes.
Maintenance Technicians: Regular maintenance of equipment, including cracking units and distillation columns, is essential to avoid production downtimes and ensure operational efficiency.
Safety Officers: Given the chemical nature of pentene production, safety is a major concern. Safety officers are responsible for implementing safety protocols and ensuring that the plant complies with local health and safety regulations.
Quality Control Technicians: Quality control personnel ensure that the produced pentene meets industry standards and is free from contaminants.
f. Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Concerns
Given the nature of pentene production, regulatory compliance and environmental concerns must be addressed at every stage. Some key regulatory aspects to consider include:
Emissions Control: The production of pentene and other petrochemicals releases gases and particles into the atmosphere. Regulations regarding emissions and air quality must be followed to reduce environmental impact.
Waste Management: Waste products from the cracking process, including unreacted hydrocarbons and by-products, must be properly managed. Implementing waste treatment systems and recycling programs can help minimize environmental damage.
Safety Standards: Due to the hazardous nature of some chemicals and processes, plants must adhere to strict safety regulations to protect workers and the surrounding community.
Product Quality Standards: Pentene production facilities must comply with various industry standards to ensure the quality and safety of their products, particularly when pentene is used in sensitive applications like pharmaceuticals or food processing.
Market Opportunities and Trends in Pentene Production
The demand for pentene is driven by various industries that use it as a precursor for chemical processes. These include plastics manufacturers, automotive companies, and the pharmaceutical and agrochemical sectors.
Some market trends influencing pentene demand include:
Increased Plastic Production: As global demand for plastics continues to rise, particularly for packaging materials, the demand for pentene used in polyethylene production is expected to grow.
Automotive Industry Growth: With an increase in demand for synthetic rubber for tires and other automotive parts, the need for pentene will continue to rise.
Environmental Considerations: Sustainability concerns are pushing for more efficient and environmentally friendly methods of pentene production. Advances in catalyst technology and process optimization are likely to shape the future of the industry.
Establishing a pentene manufacturing plant offers significant opportunities in an expanding global market. By understanding the production process, sourcing high-quality raw materials, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations, businesses can capitalize on the growing demand for pentene and its applications in industries such as plastics, automotive, and chemicals.