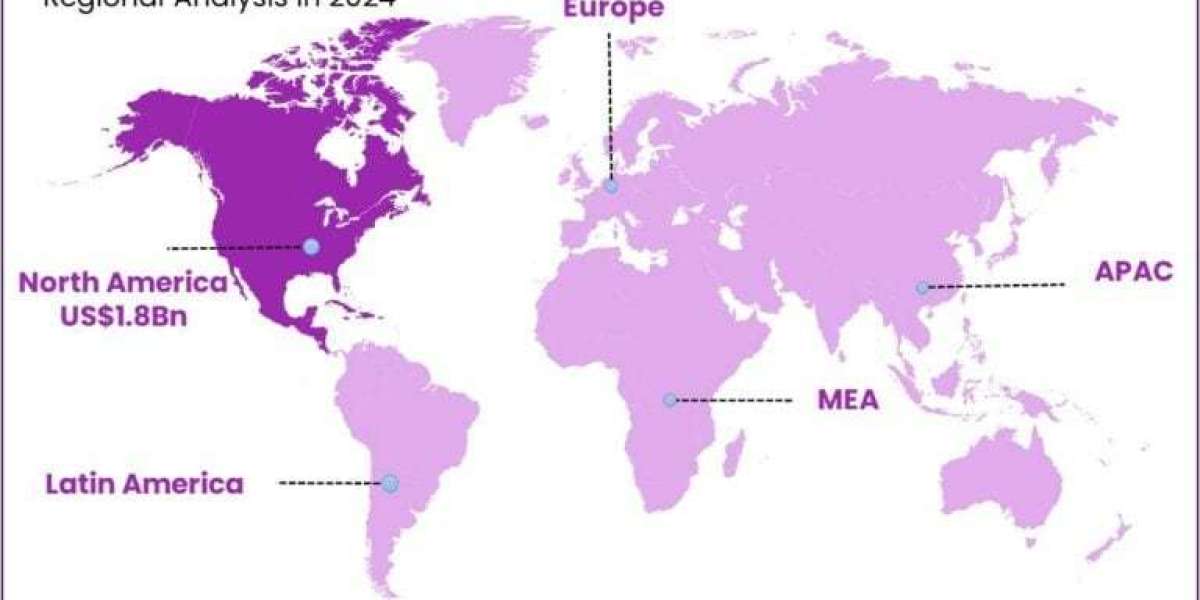
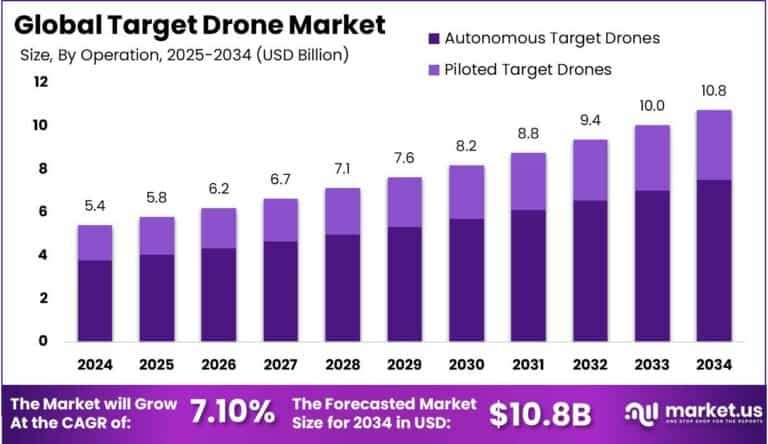
The global target drone market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.10% between 2025 and 2034, from an estimated USD 5.42 billion in 2024 to USD 10.8 billion in 2034. With over 35% of the market and USD 1.8 billion in revenue, North America dominated the target drone market in 2024. The target drone market in the United States is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% and be valued at USD 1.7 billion.
According to market.us target, a target drone is a kind of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), typically controlled by a remote control, that is primarily used for training in order to simulate enemy aircraft and test anti-aircraft defenses. They can mimic a wide range of military threats and look like radio-controlled model airplanes.
Read more information https://market.us/report/target-drone-market/
Demand Analysis
Target drone purchases are being accelerated by military forces globally in order to stay up with the latest advancements in air defense technology. Rekindled great-power tensions and the need for more practical training against advanced threats are the main causes of rising defense budgets, which are already expected to surpass €326 billion in Europe this year. Due to both large unit purchases and lengthy service agreements, North America alone accounted for more than 36% of the global target drone revenue in 2023.
Top Driving Factors
- Modernization of Defenses Forces: Matching target-drone capabilities are necessary for nations upgrading their legacy air defense systems in order to test new radars and interceptors.
- Cost Efficiency: Compared to conventional missiles, electric propulsion and reusable drones reduce the cost of each flight.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The ongoing need for realistic threat simulators is fuelled by regional conflicts and alliance-driven exercises.
Market Trends
- Autonomy & AI: Drones are increasingly equipped with machine-learning algorithms to fly unpredictable patterns, improving training realism.
- Swarming Technologies: Coordinated drone “swarms” test a base’s ability to counter simultaneous threats.
- Eco-friendly Designs: Manufacturers explore biodegradable materials and electric propulsion to reduce environmental impact
Increasing Adoption Technologies & Key Reasons
- 3D-Printed Airframes: Allow rapid prototyping and lower production costs, making custom signature drones affordable.
- Advanced Sensors & ECM Suites: Enable target drones to emulate radar-stealth fighters or jammers, offering high-fidelity training at scale.
- Secure Data Links: Hardened communications safeguard against live drills being
Organizations adopt these advances principally to boost training realism, cut lifecycle costs and flexibly adjust threat profiles on demand.
Investment Opportunities
With countries like South Korea, Japan, and India expanding their domestic drone programs and looking to diversify their training resources, Asia-Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest rate, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 10% through 2030. Joint ventures, offset agreements, and technology transfers are also made possible by alliances between regional aerospace companies and international OEMs.
Technological Advancements
Recent innovations include :
- Low-Observable Coatings that replicate stealth signatures,
- Hybrid Propulsion combining fuel and electric engines for adjustable endurance,
- On-board AI for dynamic threat generation,
all of which accelerate the shift from simple “fly-by” targets to fully programmable adversary simulators.
Regulatory Environment
National airspace regulations, stringent export controls (like ITAR in the US), and no-fly-zone restrictions all apply to target drones. Procurement procedures often require multi-year licensing and end-user certificates, which add complexity while keeping costly systems out of the wrong hands.
Top Impacting Factors
- Supply Chain Resilience: Manufacturers have diversified their suppliers as a result of COVID-19 disruptions that brought attention to their dependence on specialized components.
- Budget Volatility: Market forecasting becomes more difficult when political priorities change and purchases are accelerated or delayed.
- Geopolitical Shocks: Training tempo and equipment turnover are significantly increased by conflicts like the Russia-Ukraine war.
Business Benefits
Companies operating in the global target drone market enjoy a range of advantages that go beyond one‐off hardware sales:
1.Steady Recurring Revenue: Following the first drone deliveries, companies obtain long-term service contracts for upkeep, software updates, and mission-planning assistance, which frequently represent 30–40% of total revenue.
- High Margins on Intellectual Property: AI-driven autonomy modules, proprietary flight-control algorithms, and signature-simulation software fetch high licensing fees, increasing overall profitability.
- Cross-Selling Opportunities: Innovations in target drones—like advanced sensors or hybrid propulsion—can be adapted into surveillance, reconnaissance or combat UAV lines, creating new market avenues without starting R&D from scratch.
- Stronger Customer Loyalty: Offering end-to-end solutions (hardware + training services + analytics) deepens ties with defenses agencies, making it harder for competitors to displace incumbents.
[Key Factors with Highest Impact]
1.Geopolitical Tensions and Conflict Escalation: Shifts in international relations and sudden outbreaks of conflict (for example, heightened tensions in Eastern Europe or the South China Sea) directly drive militaries to intensify live-fire exercises. That means more target drones are ordered on short notice to mimic advanced threats and keep training realistic.
2.Defenses Budget Allocations and Procurement Cycles: Annual and multi-year defenses spending plans determine how many target drones can be bought or leased. When governments boost procurement budgets, orders rise sharply; conversely, budget cuts or re-prioritization toward cyber or space domains may delay drone acquisitions.
3.Technological Innovation Pace: Breakthroughs in autonomy, AI-driven flight control and electronic-signature simulation let target drones offer ever more lifelike threat profiles. Rapid innovation ups the value of each new drone generation, encouraging armed forces to replace older fleets sooner.
Regional Analysis
North America
With roughly 36.8% of global target drone sales in 2024, North America continues to be the largest regional market. This dominance is fuelled by the US's large defense budget, cutting-edge living-fire training programs, and robust OEM presence (e.g., Kratos, Northrop Grumman, Boeing). Strong hardware sales and steady revenue streams are ensured by the high demand for realistic threat simulators and long-term service contracts for upkeep, software updates, and mission planning.
Europe
The second-largest market, Europe, is expected to grow steadily between 2023 and 2033, with a 5.34% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), Higher defense expenditures in reaction to issues with regional security (such as tensions in Eastern Europe or NATO exercises)
Modernization initiatives in Germany, France, and the United Kingdom that require sophisticated drone targets for new air defense systems, Joint R&D projects within the frameworks of the EU and NATO.
Analysis Viewpoint
According to analysts, the global target drone market is situated at the nexus of rapidly evolving technology and high strategic importance. On the one hand, strong defined budgets and escalating geopolitical tensions ensure a stable baseline of demand; on the other hand, countries are unable to compromise on practical training against new threats. On the other hand, what was considered "state-of-the-art" just two to three years ago is rapidly becoming obsolete due to the rapid advancements in AI autonomy, swarming tactics, and signature simulation.
Businesses that make early investments in modular platforms—platforms that can accommodate new software upgrades or sensor suites without requiring an airframe redesign—are well-positioned to win the majority of new contracts by balancing these forces. Businesses must simultaneously manage intricate export regulations and strengthen their supply chains; delays in essential parts or licensing.